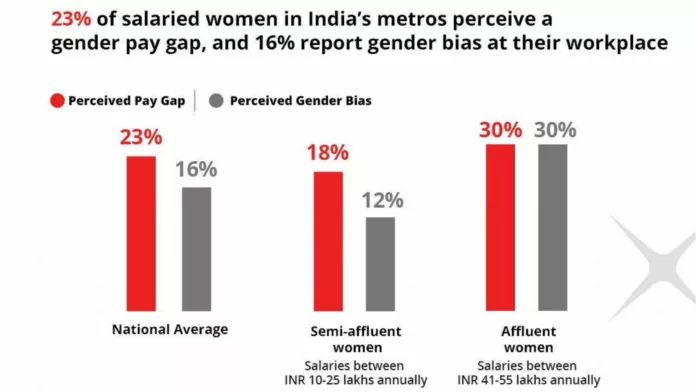
With rising affluence, the perception of gender pay gap and bias is seen to increase.
DBS Bank India, in collaboration with CRISIL, launched the second of three reports from its comprehensive study entitled ‘Women and Finance’. The report is based on a survey of over 800 salaried and self-employed women across 10 cities in India and is designed to reveal the interplay between their professional aspirations and personal lifestyle preferences.
Building upon the first part released in January 2024, the second report offers valuable insights into the unique circumstances of women in the workforce, including their professional aspirations, habits, and the barriers they face. It examines how factors like age, income, marital status, and location influence their preferences.
While salary and career advancement ranked as the topmost factors when selecting a job for 69% of salaried women, 42% of self-employed women prioritised independence and flexible working hours. Interestingly, remote working is not a high priority among salaried women, with only 3% considering it essential.
Understanding the dynamics and challenges faced by salaried women in the workforce
The findings corroborate industry views on persistent gender disparities in the workplace, revealing that the perceived gender pay gap at a pan-India level stood at 23% among salaried women, while perceived gender bias stood at 16%. Semi-affluent women, earning between ₹10 to 25 lakhs annually, and affluent women, with salaries ranging from ₹41 to 55 lakhs per year, have varying perspectives on the gender pay gap. Affluent women reported a higher perception of the gender pay gap at 30%, while this stood at 18% among semi-affluent women. A similar trend was seen with the perception of gender bias at the workplace with 30% of affluent women asserting that they had experienced it, significantly higher than the 12% of women in the semi-affluent cohort who had perceived the same bias.
42% of salaried women in metros face challenges while negotiating salaries. The experiences differ between the eastern and western parts of India. In Kolkata, 96% of salaried women do not face a challenge in negotiating their pay, while only 33% in Ahmedabad feel the same. Contrasting perspectives are also observed in southern India. In Chennai, 77% of women do not face challenges when negotiating salaries, compared to 41% in Hyderabad.
Kishore Poduri, Managing Director, and Country Head – HR, DBS Bank India said, “Encouraging the active participation of women in the workforce is crucial for fostering their economic independence and ensuring autonomy in financial decision-making. Insights gleaned from the study can empower organisations to understand women’s aspirations better and tailor strategies that align with their preferences. This can lead to more fulfilling careers for women, enhancing their participation in the workforce and maximising their potential contributions.”
“DBS embodies being a different kind of bank, and the ‘Women and Finance’ study is an extension of this ethos. Women constitute half of our global workforce and ~30% of our employee base in India. By leveraging some of the findings from this study, we can better address their diverse needs and provide support to help them thrive both personally and professionally,” he added.
Policies and initiatives preferred by salaried women
Among salaried women, those who are unmarried show a greater appreciation for mentorship and career development opportunities compared to their married counterparts. Specifically, 26% of unmarried women express appreciation for such programs, compared to 16% of married women.
Regional variations lend greater depth to the insights. For instance, in Kolkata, 46% of salaried women consider mentorship and career development programs to be the most valuable, surpassing the national average of 19%. Similarly, in Delhi, 33% of salaried women value childcare support facilities offered by organisations, compared to the national average of 11%. Among women in Chennai, 32% accord the most importance to extended maternity benefits, surpassing the national average of 19%. This aligns with the behaviours reflected within DBS Bank India’s employee base. In a recent internal survey, female employees ranked mentorship and career advancement opportunities (19%) and support for expecting mothers (16%) as the top initiatives they found most valuable.
These findings also highlight the need for organisations to implement family-friendly policies that improve work-life harmony for women with caregiving responsibilities. In Pune, 35% of salaried women consider sabbatical policies to be the most valuable, significantly higher than the national average of 5%.
Lifestyle preferences
In addition to workplace dynamics, the report delves into the multifaceted lifestyle preferences of women and provides insights into their spending preferences and habits around health & wellness, dining, and leisure travel. The study reveals that female earners in India’s metros prioritise health despite their busy schedules, with 66% undergoing comprehensive health check-ups in the past year. A similar trend was observed among women at DBS Bank India, where 57% of respondents in an internal survey reported having undergone comprehensive health check-ups during the same period.
Only 32% dine out or order food more than once a week, while just 24% of women spend more than four hours daily on non-office screen time. This underscores the opportunity for organisations to enhance their offerings, prioritising initiatives that promote holistic well-being for this demographic.
32% of married women took 3-5 leisure trips in the past year, which is twice as many as their unmarried counterparts, challenging the myth that married women go for fewer leisure trips than unmarried women. Nearly half of the surveyed women (47%) were generous spenders, who spend more than 70% of their income. The survey findings further reveal that 39% of women from this segment have high credit card spends in discretionary categories namely travel and shopping, compared to the pan-India average of 33%.
DBS has been an integral part of India since 1994, and it is the largest foreign bank in the country by branch presence, with a physical footprint of around 530 branches in 350 locations. It brings simplicity and seamlessness to banking through its suite of solutions and is a trusted partner for small, medium, and large businesses as well as retail customers. Reinforcing its brand promise of “Live More, Bank Less,” DBS Bank India endeavours to support holistic financial management for women, guided by insights from the Women and Finance study.
